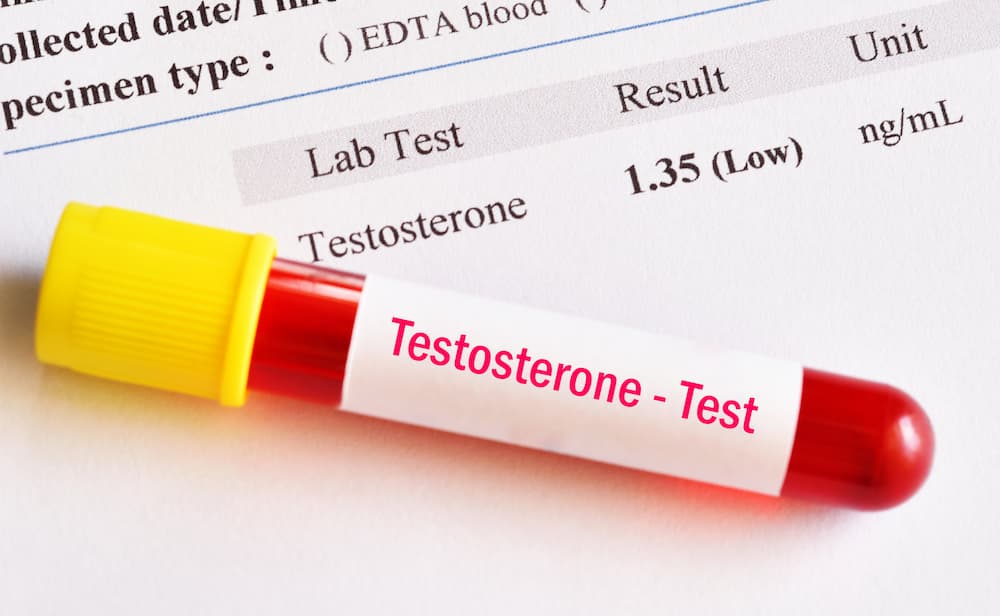
Millions of men in the U.S. are affected by low testosterone and its wide range of frustrating side effects, all of which can make it difficult to enjoy life in your 40s, 50s, and beyond. And yet, a surprising number of people aren’t aware of the common causes and symptoms of low testosterone – which is why many men go undiagnosed and untreated.
Understanding low-T causes can help you make sense of “mystery” symptoms that you might have otherwise attributed to aging. Even more importantly, pinpointing a low testosterone cause is an essential first step towards getting treatment that actually works for you.
In this post, we’re going to cover some of the factors that can cause low testosterone levels, including the most common contributors and a few that are usually rarer. We’ll also talk about some signs of low testosterone, and what you can do if you suspect you have low-T.
What is Low Testosterone?
Low testosterone is exactly what it sounds like: low levels of testosterone, an important hormone that serves a variety of purposes in the male body.
Testosterone is the hormone that kicks puberty into gear, helps you grow from a teen boy into an adult man, and powers many different aspects of “masculinity.” From your muscle mass and physical stamina to your sex drive and ability to concentrate, the way you look and feel is significantly impacted by your testosterone levels.
A normal range for testosterone levels usually falls between 300 and 1,000 ng/dL, according to information from the FDA. A diagnosis of low testosterone, or low-T, can be made when levels are below 300. Your hormone doctor will use a blood test (known as a serum testosterone test) to assess how much testosterone is circulating through your body.
Causes of Low Testosterone
Low-T is often thought of as a condition that only affects older men. However, there are so many different causes of testosterone deficiency that men of all ages can end up facing this frustrating issue.
Medical professionals typically organize low-T, also called hypogonadism, into two categories:
- Primary hypogonadism
- Secondary hypogonadism
Primary hypogonadism
In simplest terms, primary hypogonadism is low-T caused by underactive testes. Testosterone is produced in the testes, so under activity can lead to low levels that impair your health or quality of life. The cause of underactive tests can be either an inherited condition or an illness/accident.
Inherited conditions that can cause underactive testes to include:
- Undescended testicles
- Klinefelter’s syndrome
- Hemochromatosis
Alternatively, certain types of injuries or illnesses can damage the testicles and cause hypogonadism:
- Physical injury to (both) testicles
- Mumps infection
- Cancer treatment (radiation/chemotherapy)
Secondary hypogonadism
Low-T due to secondary hypogonadism is connected to a damaged pituitary gland or hypothalamus, which are two of the “control centers” behind hormone production. Secondary hypogonadism can be linked to a genetic condition, or it can be caused by other circumstances.
Inherited conditions or illnesses contributing to secondary hypogonadism include:
- Pituitary disorders (related to small tumors, kidney failure, drug use, or other conditions)
- Kallmann syndrome
- Inflammatory diseases (tuberculosis, histiocytosis, and others)
- HIV/AIDS
There are also certain circumstances that can lead to secondary hypogonadism:
- Aging
- Obesity
- Some medications (steroids and opioid pain medications)
- Emotional/physical stress from illness or surgery
Diagnosing low-T and hypogonadism
You could have primary or secondary hypogonadism or even a combination of both. In addition to the factors listed above, there are also many other reasons your T-levels could be falling short. This makes it important to get a professional assessment and consultation before trying any treatments.
How to Know If You Have Low Testosterone Symptoms
Once you turn 30, testosterone production starts to decline. For a small number of men, their bodies are still able to maintain a T-level that falls within the estimated normal range. But for 40% of men or more, the slowed rates of production can lead to a deficiency.
This means that many men with low testosterone can attribute it to getting older – but because of this, the tell-tale signs are often mistakenly seen as side effects of aging.
Here are some key signs you should consider low-T red flags, so you can get assessed and pursue treatment if needed:
- Low energy levels
- Unexplained weight gain
- Increased fat buildup, especially around your gut
- Losing muscle
- Feeling irritable, depressed, or anxious
- Having a hard time focusing or finding motivation
- Decreased sex drive
- Issues with erectile dysfunction (ED)
Treat Low-T with TRT from EHormones MD
Finding out what causes low-T is just the first step – but Ehormones MD can help you from the beginning of your journey on. We’ll evaluate your T-levels, pinpoint potential causes, and set you up with an effective plan to restore testosterone deficiencies with testosterone replacement treatment (TRT) and other strategies.
Learn more about how TRT helps low-T when you contact the EHormones team today!
Image Source: Jarun Ontakrai / Shutterstock